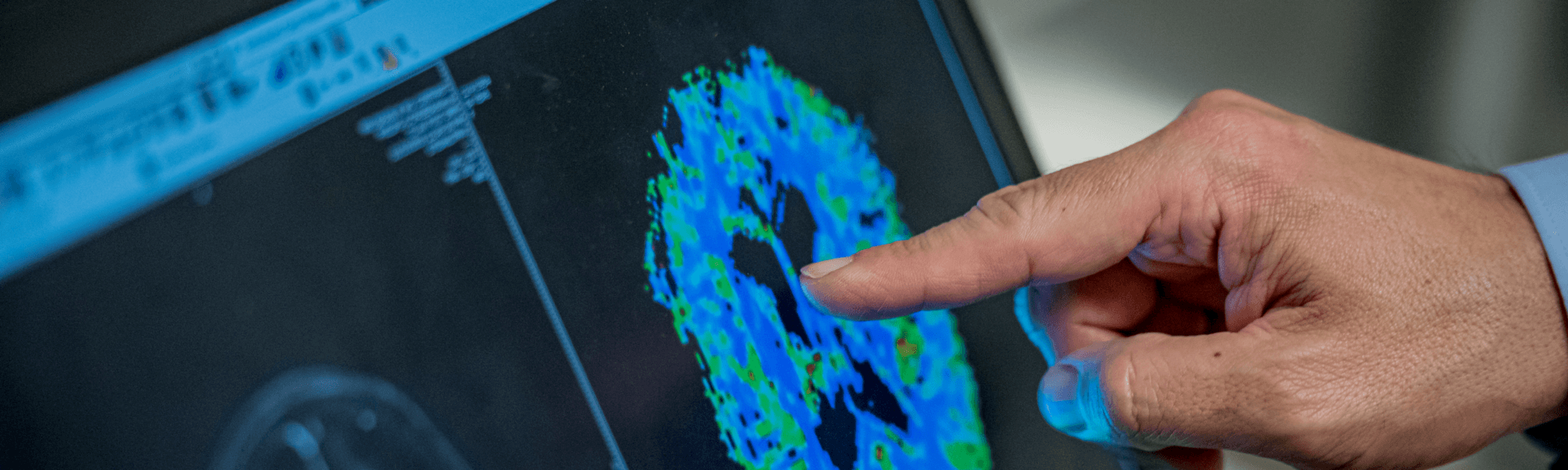
Cystoperitoneal Shunt
Written and reviewed by:
We are a highly specialized team of medical professionals with extensive neurological and cranial disorder knowledge, expertise and writing experience.
Last updated: April 6, 2020

