Intracranial Meningioma, the Most Common Type of Brain Tumor
by PNI Experts
Daniel F. Kelly, MD, Founder and Director of Pacific Neuroscience Institute (PNI), explains the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment for intracranial meningiomas, the most common type of benign brain tumor.
With more than 120 different types of brain tumors, it can be difficult to differentiate between benign and malignant brain tumors. At Pacific Brain Tumor Center at Pacific Neuroscience Institute (PNI) our team of highly-skilled radiation oncologists, neuro-oncologists, medical oncologists, and neurosurgeons, are experts in diagnosing and treating both benign and malignant brain tumors.
Brain tumors are masses of abnormal growth in the tissues of the brain. Brain tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant, meaning that they have cancer cells that grow rapidly. Brain tumors that start in the brain are called primary brain tumors, while tumors that start elsewhere in the body and move to the brain are called metastatic brain tumors.
What is an intracranial meningioma?
Intracranial meningiomas are primary brain tumors, meaning that they start in the brain. Intracranial meningiomas are the most common type of benign brain tumor that develops or arises from any meningeal surface of the brain. Intracranial meningiomas are typically attached to the dura (outer layer of the meninges), but can also occur in the cerebral ventricles.
What are the symptoms of an intracranial meningioma?
Intracranial meningiomas can cause a variety of symptoms due to the fact they occur in many different places across the head. Symptoms of intracranial meningiomas include:
- Vision loss
- Double vision
- Headache
- Seizure
- Difficulty swallowing
- Hearing loss
If you or your loved one suspect that you may have a brain tumor, don’t wait. Seek medical attention if you are experiencing symptoms of a brain tumor.
What is the best treatment for an intracranial meningioma?
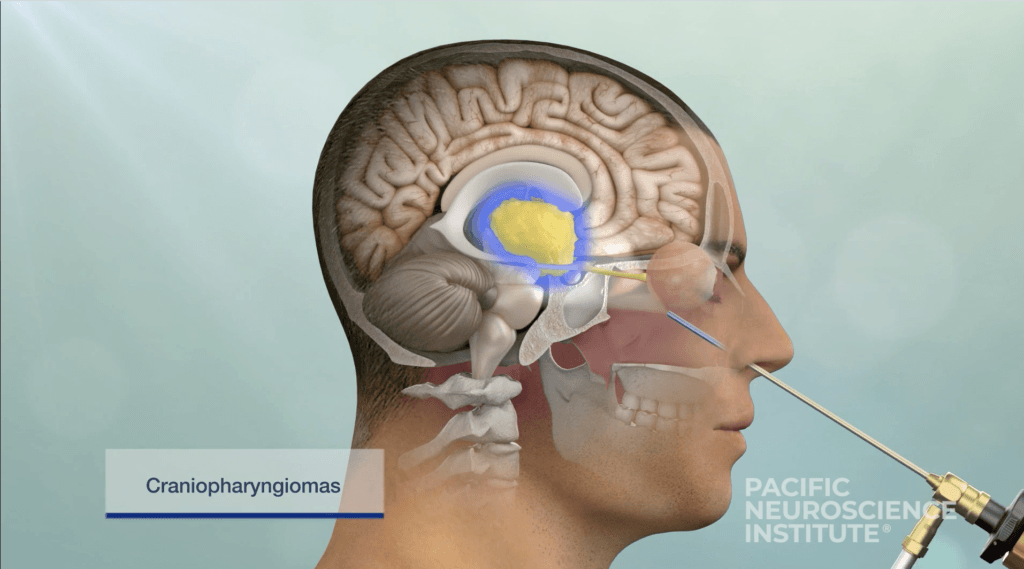
Optimal treatment for intracranial meningiomas is determined by the location. However, in virtually all symptomatic meningiomas, the treatment is surgical removal. At PNI, experts have extensive experience in the minimally invasive removal of intracranial meningiomas using a variety of keyhole approaches. These treatment approaches include:
- Endoscopic endonasal approach (through the nostrils)
- Superorbital eyebrow approach (through a small incision through the eyebrow)
- Minipterional approach (an incision just behind the hairline)
- Transorbital approach
Other approaches include behind the ear and along the top of the head, depending upon where the tumor occurs.
What happens if an intrancranial meniogioma is not entirely removed?
The goal is always maximal safe removal. In some cases, since meningiomas may be very adherent to some of the cranial nerves, the brain itself, or critical blood vessels, we have to leave behind a small amount of the tumor. We do that to ensure that the patient comes out of surgery better than they went in, preserving the quality of life and not with new neurological problems.
Fortunately, most meningiomas are radiosensitive, meaning that they can respond well to focused radiation treatment. In patients who were not able to get a complete removal, sometimes focus radiation is needed. Overall, the diagnosis of meningioma, although somewhat scary, is one that can be dealt with very effectively in skilled hands using keyhole and minimally invasive approaches.
About Pacific Brain Tumor Center
At Pacific Brain Tumor Center at Pacific Neuroscience Institute, we have one of the world’s largest experiences in minimally invasive surgery and non-surgical treatment for such tumors, including novel therapies and clinical trials. Our comprehensive team approach which includes our radiation oncologists, neuro-oncologists, medical oncologists, and neurosurgeons, allows for a refined treatment plan for each patient.
If you, a family member, or a friend have been diagnosed with a brain or skull base tumor, our team of experts is here to provide help and guidance. We provide comprehensive care for these challenging problems as well as patient education and psychosocial support.
About Dr. Daniel Kelly

Daniel F. Kelly, MD, a board-certified neurosurgeon, is the Director and one of the founders of the Pacific Neuroscience Institute, Director of the Pacific Brain Tumor Center and Pacific Pituitary Disorders Center, and is a Professor of Neurosurgery at Saint John’s Cancer Institute at Providence Saint John’s Health Center. Considered to be one of the top neurosurgeons in the US, he has been awarded the Southern California SuperDoctors distinction 15 years in a row. A multiple recipient of the Patients’ Choice Award, Dr. Kelly is internationally recognized in the field of minimally invasive keyhole surgery for brain, pituitary and skull base tumors. In practice for over 25 years, he has one of the world’s largest series in endonasal surgery with over 2,000 procedures performed including over 900 endoscopic endonasal surgeries, and almost 2,000 craniotomies for brain and skull base tumors.
Useful Links
About the Author
PNI Experts
Last updated: December 6th, 2022
