Largest Study of Brain Tumor “Keyhole” Surgery for Meningiomas
by PNI Experts
Pacific Neuroscience Institute Sets New Standard of Excellence in Minimally Invasive Keyhole Surgery
SANTA MONICA (Aug. 3, 2022) – In a groundbreaking 13-year study, Pacific Neuroscience Institute neurosurgical and otolaryngology surgical teams demonstrated outstanding outcomes with minimally invasive keyhole surgery for the most common primary brain tumor, in the largest such keyhole cohort published to date.
The meningioma study, conducted in collaboration with Providence Saint John’s Health Center, was published in the July 28 issue of PLOS ONE. Findings demonstrate a combination of excellent tumor removal rates, lower surgical complication rates and a higher rate of functional preservation, compared to prior publications of intracranial meningioma surgery using more traditional approaches.
“Patients coming to us with brain tumors are understandably worried about their diagnoses and clinical outcomes,” said neurosurgeon Daniel Kelly, MD, PNI director and senior author of the study. “Keyhole surgery aims to limit brain exposure and manipulation, using smaller strategically placed openings without the use of brain retractors and facilitated by gravity assistance and endoscopy. These techniques, along with improved neuro-anesthesia and our growing experience, benefit our patients by allowing, in most cases, a faster recovery, shorter hospital stay and rapid return to daily activities.”
About Meningiomas
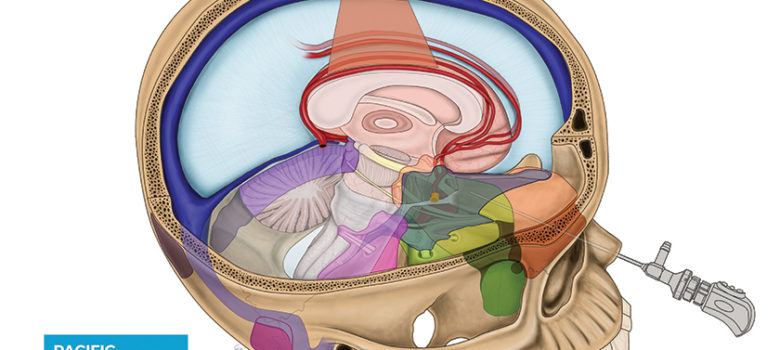
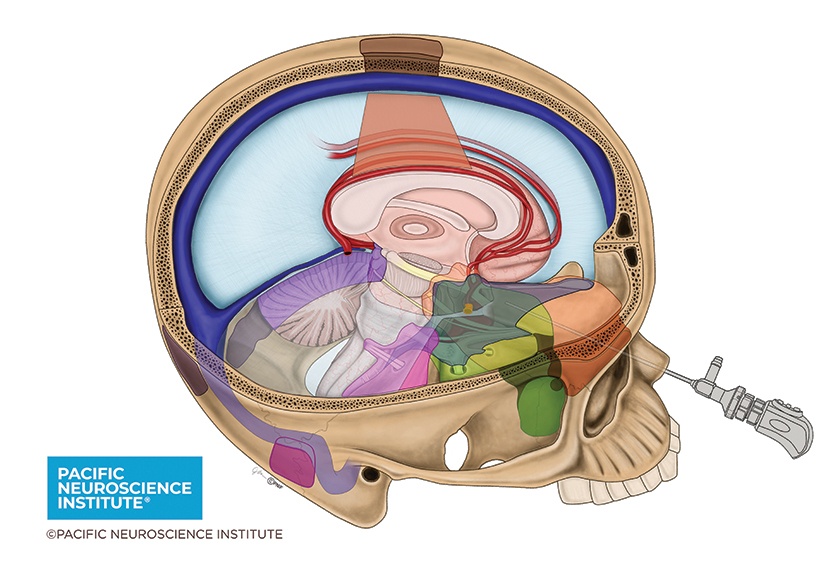
Meningiomas, the most common primary brain tumor, are non-cancerous brain tumors estimated to be diagnosed in approximately 34,000 people in the United States each year. Surgery for meningiomas has evolved over the last 20 years from traditional larger open craniotomies to an increase in smaller, minimally invasive approaches, including through the natural openings of the nostrils (endonasal), through an eyebrow incision (supraorbital) and other small incisions often with the assistance of a high-definition endoscope (flexible microsurgical telescope). PNI’s surgical team has helped lead this evolution in keyhole surgery for all brain and skull base tumors, with an overarching goal of maximal safe tumor removal and preservation of neurological function.
Study Results
From an overall cohort of 329 patients with meningiomas treated from 2008-21, the study focused on 193 (59%) who underwent 213 keyhole operations. Keyhole approaches included endoscopic endonasal, supraorbital eyebrow, mini-pterional, retromastoid, supracerebellar and transfalcine.
Compared to prior publications of meningioma surgery using more traditional, larger approaches, there were lower rates of permanent neurological deficits (6%), cerebrospinal fluid leaks (1%) and meningitis (1%). Notably, 94% of patients were discharged to home, and no patients sustained post-operative deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary emboli or myocardial infarction. There were no deaths within 30 days of surgery. Hospital length-of-stay also was considerably shorter (median three days) compared to most prior reports, and decreased to two days in the last two years of the study.

“Although most meningiomas are slow-growing benign tumors, they often become adherent to blood vessels, cranial nerves, and can invade the skull base, said neurosurgeon Garni Barkhoudaian, MD, chief of the radiosurgery program and co-author of the study. “Consequently, aiming for maximal safe removal is critical to the keyhole concept because attempting complete removal in some locations can come at a high risk of major complications.
“Here at PNI, we strive to avoid such complications while still achieving excellent tumor removal rates. Fortunately, most meningiomas that cannot be removed completely can be observed over time or treated effectively and safely with focused radiation or radiosurgery.”
The article is published in PLOS ONE.
Article Source: Critical appraisal of minimally invasive keyhole surgery for intracranial meningioma in a large case series
Thakur JD, Mallari RJ, Corlin A, Yawitz S, Eisenberg A, et al. (2022) Critical appraisal of minimally invasive keyhole surgery for intracranial meningioma in a large case series. PLOS ONE 17(7): e0264053. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0264053
About Dr. Daniel Kelly

Daniel F. Kelly, MD, a board-certified neurosurgeon, is the Director and one of the founders of the Pacific Neuroscience Institute, Director of the Pacific Brain Tumor Center and Pacific Pituitary Disorders Center, and is a Professor of Neurosurgery at Saint John’s Cancer Institute at Providence Saint John’s Health Center. Considered to be one of the top neurosurgeons in the US, he has been awarded the Southern California SuperDoctors distinction 15 years in a row. A multiple recipient of the Patients’ Choice Award, Dr. Kelly is internationally recognized in the field of minimally invasive keyhole surgery for brain, pituitary and skull base tumors. In practice for over 25 years, he has one of the world’s largest series in endonasal surgery with over 2,000 procedures performed including over 900 endoscopic endonasal surgeries, and almost 2,000 craniotomies for brain and skull base tumors.
About Dr. Garni Barkhoudarian

Garni Barkhoudarian, MD, FAANS, is a board-certified, fellowship-trained neurosurgeon with a focus on skull base and minimally invasive endoscopic surgery. Dr. Barkhoudarian has particular interest and expertise in pituitary and parasellar tumors, brain tumors, skull-base tumors (including meningiomas, craniopharyngiomas, chordomas and schwannomas), intra-ventricular brain tumors, colloid cysts, trigeminal neuralgia, hemifacial spasm and other vascular compression syndromes.
Useful Links
About the Author
PNI Experts
Last updated: August 17th, 2022