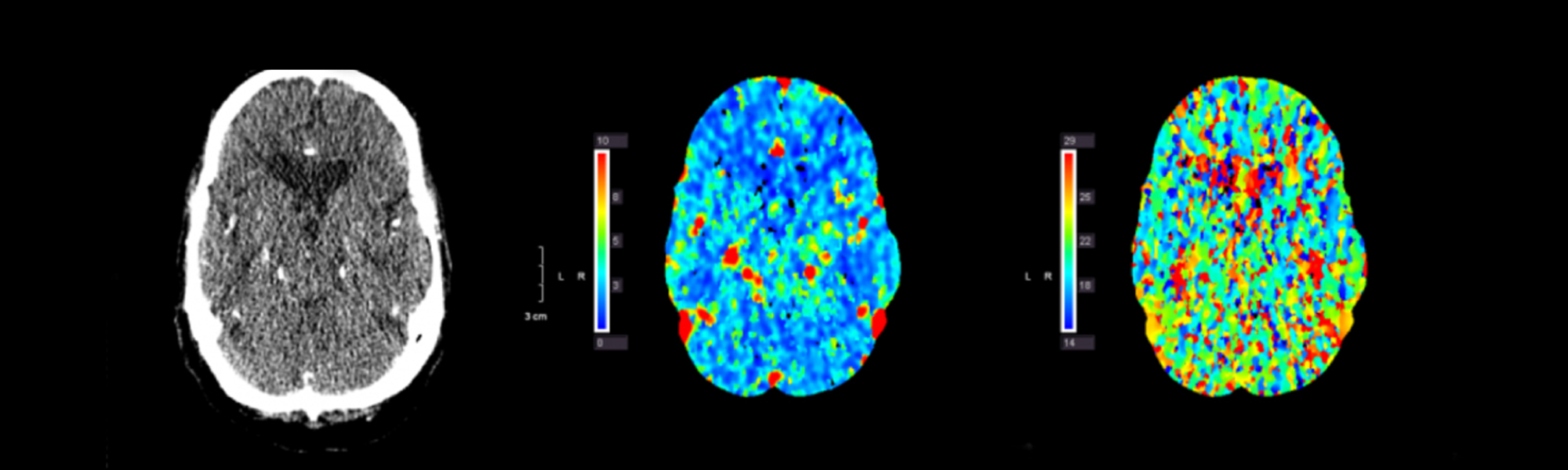
Ischemic Stroke
Ischemic stroke is the most common type of stroke occurring in 87% of patients.
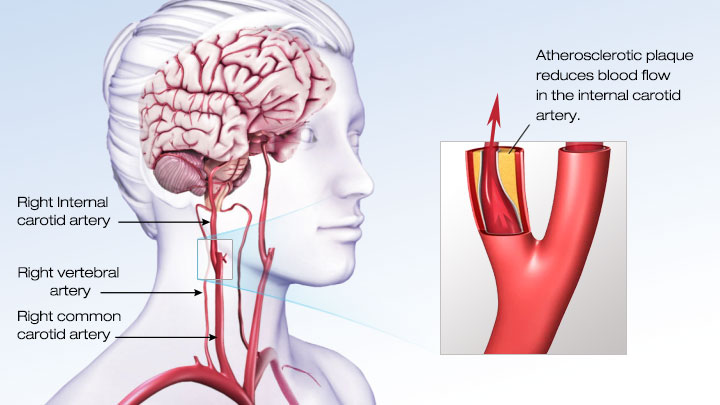
An ischemic stroke occurs when an artery in the brain is blocked.
The blockage can occur when a blood clot or plaque fragment forms, usually in the heart or the large arteries leading to the brain and then moves through the arteries to the brain. A thrombotic stroke is a blood clot that forms inside an artery in the brain. The clot interrupts blood flow and causes a stroke.
Symptoms of Ischemic Stroke
Some signs of ischemic stroke include:
- Sudden numbness or weakness of the face, arm or leg, especially on one side of the body
- Sudden confusion, trouble speaking or understanding
- Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes
- Sudden trouble walking, dizziness or loss of balance
- Sudden severe headache with no known cause
If you have any of these symptoms or see someone else having them, call 9-1-1 immediately.
Treatment of Ischemic Stroke
Fast treatment of ischemic stroke at the hospital can lead to better results. Treatment of ischemic stroke includes the administration of clot busting medication and if indicated the use of a stent retriever to remove the blood clot.
We use the most current and rapid evaluation techniques to deliver tissue plasminogen activator (tPA, also known as IV rtPA, administered through an IV in the arm) in patients having an ischemic stroke. tPA dissolves the blood clot allowing the blood to flow more freely to the affected part of the brain. As circumstances permit, we try to administer tPA within 3 hours (and up to 4.5 hours in certain eligible patients), which improves the chances of recovering from a stroke. A significant number of ischemic stroke patients are unable to get to a hospital in time for tPA treatment reducing the success rate of treatment.
Minimally-Invasive Ischemic Stroke Surgical Procedure

Our experts specialize in the use of an endovascular procedure called mechanical thrombectomy to treat ischemic stroke. For patients who are eligible for this procedure, our physicians remove the lodged blood clot obstructing the blood vessel in the brain using a wired cage-like device called a stent retriever. A catheter with the stent retriever attached to its end is threaded through an artery in the groin up to the blocked artery in the brain.
The wire meshing opens to surround the clot and the stent is removed along with the trapped clot. The procedure can be conducted after a patient receives tPA and should be done as soon as possible after stroke symptoms occur.
Read Other Blog articles about Stroke
Contact Us
The Pacific Stroke and Neurovascular Center’s state-of-the-art facilities are located at:
Providence Saint John’s Health Center
2125 Arizona Ave., Santa Monica, CA 90404
310-829-8319
Providence Little Company of Mary Medical Center Torrance
4201 Torrance Blvd., Suite 520, Torrance, CA 90503
424-212-5340
Providence Saint Joseph Medical Center
501 S. Buena Vista Ave., Burbank, CA 90505
818-847-6049
Providence Holy Cross Medical Center
15031 Rinaldi St, Mission Hills, CA 91345
818-847-6570